Pablo E. Castillo, M.D., Ph.D.
Professor, Dominick P. Purpura Department of Neuroscience Harold and Muriel Block Chair in Neuroscience
(neuroscience category)

Synaptic transmission underlies every aspect of nervous system function. How we think, feel, act and learn, all rely on information transfer between nerve cells. In addition, synapses are extremely dynamic, and activity-dependent changes in synaptic strength are essential to most forms of learning. It is becoming increasingly clear that synaptic dysfunction is central to the etiology and progression of a wide range of neuropsychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders. The main goal of my research program is to understand the cellular and molecular basis of activity-dependent changes in synaptic strength at both excitatory and inhibitory connections, and how such changes are modified during pathological conditions. In our studies we use brain slice electrophysiology and pharmacology, two-photon laser microscopy, optogenetics and a wide-range of molecular manipulations. To gain insights into the mechanisms of synaptic function, we include in our studies functional analyses of transgenic mice for several synaptic proteins, as well as mouse models for various neuropsychiatric conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease, autistic spectrum disorders and schizophrenia.
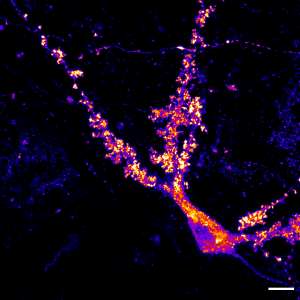
Mossy cell in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus expressing labelled actin in its large postsynaptic structures, the thorny excresences.
Selected Publications
Hashimotodani Y, Nasrallah K, Jensen KR, Chávez AE, Carrera D, Castillo PE. (2017) LTP at Hilar Mossy Cell-Dentate Granule Cell Synapses Modulates Dentate Gyrus Output by Increasing Excitation/Inhibition Balance. Neuron 95:928-9.
Monday HR and Castillo PE (2017) Closing the gap: long-term presynaptic plasticity in brain function and disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol 45:106-112.
Younts TJ, Monday HR, Dudok B, Klein ME, Jordan BA, Katona I, Castillo PE. (2016) Presynaptic Protein Synthesis Is Required for Long-Term Plasticity of GABA Release. Neuron 92:479-492.
Park J, Chávez AE, Mineur YS, Morimoto-Tomita M, Lutzu S, Kim KS, Picciotto MR, Castillo PE, Tomita S. (2016) CaMKII Phosphorylation of TARPγ-8 Is a Mediator of LTP and Learning and Memory. Neuron. 2016 Oct 5;92(1):75-83.
Jurgensen S, Castillo PE. (2015) Selective Dysregulation of Hippocampal Inhibition in the Mouse Lacking Autism Candidate Gene CNTNAP2. J Neurosci 35:14681-7.
Klein ME, Castillo PE, Jordan BA (2015) Coordination between translation and degradation regulates inducibility of mGluR-LTD. Cell Reports 10:1459–66.
Younts TJ, Castillo PE (2014) Endogenous cannabinoid signaling at inhibitory interneurons. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 26:42-50.
Klein ME, Younts TJ, Castillo, PE, Jordan, BA (2013) RNA-binding protein Sam68 controls synapse number and local β-actin mRNA metabolism in dendrites. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA. 110(8):3125-3130.
Kaeser-Woo YJ, Younts TJ, Yang X, Zhou P, Wu D, Castillo PE, Südhof TC (2013) Synaptotagmin-12 phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent protein kinase is essential for hippocampal mossy fiber LTP. J. Neurosci. 33(23):9769-9780.
Younts TJ, Chevaleyre V, Castillo PE (2013) CA1 pyramidal cell theta-burst firing triggers endocannabinoid-mediated long-termdepression at both somatic and dendritic inhibitory synapses. J. Neurosci. 33:13743-13757.